Unique Tips About What Is The Difference Between 2 Phase And 3-phase

What Is Three Phase Vs Single At Felipe Heidt Blog
Understanding Electrical Power
Ever wondered how the lights in your house turn on, or how that giant industrial machine gets its juice? Electricity is the answer, obviously, but the way it's delivered can vary. Two common methods are 2-phase and 3-phase power. While most homes use single-phase, understanding the difference between 2-phase and 3-phase systems is key to grasping how power works in different settings. It's like knowing the difference between a bicycle and a motorcycle — both get you around, but they operate on different principles and are suited for different tasks.
1. What's the Basic Idea?
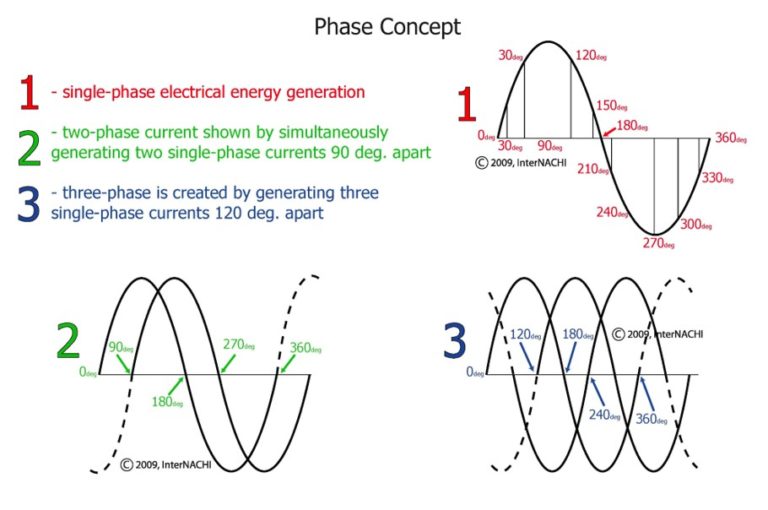
Think of electricity as water flowing through pipes. In a single-phase system (which we wont deep dive into here), it's like one pipe delivering water. In a 2-phase system, imagine two pipes delivering water, but their flow is staggered. And in a 3-phase system, you have three pipes with staggered water flow. This staggering, technically called "phase difference," is the secret sauce that makes the higher-phase systems more efficient for certain applications.
The important takeaway is that more phases generally translates to a smoother and more consistent power delivery. Its a bit like having multiple people pushing a swing — if they all push at slightly different times, the swing maintains a smoother, more consistent motion than if just one person were pushing intermittently. This consistency is super helpful for larger motors and industrial equipment.
While 2-phase used to be more common in some older applications, today you'll more often see 3-phase used, especially in industrial settings. So, lets get into the specifics of why that is.
The subtle art of power distribution is an interesting area where the advantages of one type of electrical distribution over another can be a game changer.
Commercial Electrical Systems What Is ThreePhase Power? CCPIA
Diving Deeper
So, what are the practical distinctions between these two systems? It boils down to a few crucial factors that impact performance, efficiency, and suitability for different uses.
2. Efficiency and Power Delivery
Here's a big one: 3-phase systems generally deliver power more efficiently than 2-phase systems. Remember the multiple people pushing the swing analogy? The staggered phases in a 3-phase system create a more constant power flow. This reduces the "pulsing" effect you might see in a 2-phase system, leading to smoother operation of motors and other equipment. This smoother operation also translates to less stress on the equipment and potentially longer lifespans.
In terms of power capacity, 3-phase systems can typically deliver more power with the same size wires compared to a 2-phase system. This is because the power is distributed more evenly across the three phases. Imagine you have three buckets carrying water instead of two, naturally you can carry more at a time! That's essentially what's happening with a 3-phase system.
It's not just about raw power, it's also about how efficiently that power is delivered. 3-phase shines here, making it the preferred choice for heavy-duty applications like running large manufacturing plants or powering massive HVAC systems.
Therefore, if efficiency and power are the key features you are considering, then 3-phase is your best bet, and its superior to the 2-phase system.
3. Complexity and Wiring
Wiring complexity is also a factor. 2-phase systems generally require fewer wires than a comparable 3-phase system. This might seem like a win for 2-phase, but the simpler wiring comes at the cost of reduced efficiency and power capacity. Plus, the slightly more complex wiring of a 3-phase system is generally a well-understood and manageable challenge for experienced electricians.
The number of components can also affect maintenance. Fewer components might translate into a slightly easier time with maintenance in some 2-phase setups. However, the overall robustness and widespread availability of parts for 3-phase systems often outweigh this advantage. Also with 3-phase system, it is built to handle more load, the frequency for maintenace may be less that the 2-phase system.
It's a bit like choosing between a simple bicycle and a more sophisticated motorcycle. The bicycle is easier to maintain, but the motorcycle offers much more power and capability.
In today's world, wiring and system complexity are rarely the deciding factor since experienced electricians can handle both quite well.
4. Applications
Where do you typically find each system? 2-phase systems were more common in the past for certain industrial applications, particularly with some older types of motors. However, with advances in technology and the clear benefits of 3-phase, 2-phase has largely been phased out. (pun intended!).
3-phase is the undisputed champion for heavy industrial applications. Think of factories, large-scale HVAC systems, water pumps, and any equipment requiring significant horsepower. The consistent power delivery and high efficiency of 3-phase make it ideal for these demanding jobs. It's also increasingly used in large commercial buildings and even some modern residential complexes with very high power demands.
While 2-phase system were used primarily for industrial purposes in the past, today the 3-phase system is used widely.
2-Phase systems today are found more commonly in niche cases, or in legacy equipment, and these uses are becoming more rare and far between.

What Is Phase In Electricity? Are Single And Three
Why 3-Phase Became the Standard
There's a good reason why 3-phase has become the dominant choice for most power-hungry applications. It's not just about the extra phase; it's the combination of factors that make it superior in many ways.
5. Efficiency Wins the Day
At the heart of it, the efficiency advantage of 3-phase is hard to ignore. By delivering power more smoothly and consistently, it minimizes energy waste and allows equipment to operate more effectively. In an era where energy conservation is crucial, this efficiency edge is a major selling point.
Think about it like this: Imagine two engines, one with a super smooth power delivery and another that sputters and stalls. The smoother engine will obviously be more efficient in converting fuel into motion. That's similar to how 3-phase maximizes the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical work.
This also translates into cost savings over the long run. Less energy wasted means lower electricity bills, which can be a significant factor for businesses and industrial facilities.
There are plenty of benefits for 3-phase systems, and that's why its dominating over the 2-phase systems.
6. Scalability and Power Capacity
As power demands increase, the scalability of 3-phase becomes even more important. It's simply easier and more cost-effective to increase the power capacity of a 3-phase system compared to a 2-phase system. This is essential for growing businesses and industries that anticipate needing more power in the future.
Consider a factory that plans to add new production lines and equipment. Upgrading the electrical system to accommodate the increased load will be much simpler and more economical with a 3-phase system already in place.
The capability of a 3-phase system to scale helps growing businesses keep up with growing demands.

Looking Ahead
While 3-phase is currently the dominant force, the landscape of power distribution is constantly evolving. New technologies and approaches are emerging, and it's worth considering what the future might hold.
7. The Rise of Smart Grids
Smart grids, with their advanced monitoring and control capabilities, are changing the way power is managed and distributed. These intelligent grids can optimize power flow, reduce outages, and improve overall system efficiency. They can work with various power distribution systems, including 3-phase, to make them even more effective.
Imagine a smart grid that can automatically adjust power flow based on real-time demand. During peak hours, it might redirect power to areas with the highest need, ensuring that everyone has access to the electricity they require. This level of dynamic control is a key feature of smart grids.
Smart grid implementation helps improve the efficiency and flow of all the different phases of energy system in the market.
8. Renewable Energy Integration
The increasing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power is also impacting power distribution. These sources often generate power intermittently, which can create challenges for maintaining grid stability. 3-phase systems, with their inherent stability and efficiency, can help to integrate these renewable sources more effectively.
Think about a solar farm connected to the grid. The amount of electricity it generates can vary depending on the weather. A robust 3-phase system can help to smooth out these fluctuations and ensure a consistent supply of power to consumers.
The 3-phase power system can provide help for the integration of renewable energy sources. The future of power distribution is going to be more sophisticated.

What Is AC Motor? Single Phase Motor Three YouTube
