Cant Miss Takeaways Of Info About What Is The Loop Current Rule
Delving into the Mysteries of the Loop Current Rule
1. Understanding Ocean Dynamics
Ever wondered about those swirling patterns you sometimes see on weather maps near the Gulf of Mexico? Well, there's a good chance you're looking at the Loop Current! It's a major player in the ocean's circulatory system, and understanding it is crucial for everything from predicting hurricane intensity to protecting marine life. Its not just some random squiggle in the water; it follows certain predictable behaviors, some of which are defined (loosely) by what we might call the "Loop Current rule," though it's more of an observed tendency than a hard-and-fast regulation.
Think of the Loop Current as a river within the ocean. It's a warm current of water that enters the Gulf of Mexico through the Yucatan Channel, loops around (hence the name!), and then exits through the Florida Straits, eventually becoming part of the Gulf Stream. It's this looping path thats key to understanding its influence and what governs its behavior, and how we can predict it.
Now, there's no single, codified "Loop Current rule" written down in some oceanographer's handbook. Instead, the phrase really refers to a complex set of factors that scientists use to understand and, hopefully, anticipate the current's movements, intensity, and its occasional nasty habit of shedding off eddies.
So, when you hear about the Loop Current "rule," picture a collection of scientific observations, computer models, and good old-fashioned oceanographic experience all working together. It's less of a simple equation and more of a very sophisticated weather forecast, but for the ocean.

What Influences the Loop Current's Behavior?
2. Key Factors at Play
Okay, if there's no official "rule," what does determine how the Loop Current behaves? Several factors come into play. One major influencer is the flow of water through the Yucatan Channel. The stronger the inflow, the more likely the Loop Current is to extend further north into the Gulf. It's like pouring more water into a bend in a river; it naturally expands.
Another crucial element is the shape of the Gulf of Mexico itself. The continental shelf and the deep-water areas create boundaries that affect the current's path. The topography under the water influences everything. The shape and depth of the seafloor act as underwater guide rails.
Also, we need to consider the density differences between the warm Loop Current water and the cooler surrounding waters. These differences create pressure gradients that influence the current's strength and direction. Warmer water is less dense, remember your highschool science?
Finally, wind patterns and atmospheric conditions can also have an impact, albeit a less direct one. Strong winds can push surface waters around, affecting the overall circulation patterns in the Gulf, and, in turn, impacting the Loop Current. It's all connected.

The Dreaded Eddy Shedding!
3. When the Loop Current Gets Moody
One of the most important things to understand about the Loop Current is its tendency to "shed" eddies. These are large, swirling masses of warm water that break off from the main current and drift westward across the Gulf. Think of it like a pot on the stove, sometimes it overflows!
These eddies can be a huge problem for hurricane prediction. Why? Because warm water is fuel for hurricanes. When a hurricane passes over a Loop Current eddy, it can rapidly intensify, leading to more powerful storms and increased damage. It's what keeps the hurricanes going strong.
Predicting when the Loop Current will shed an eddy, and where that eddy will drift, is a major challenge for oceanographers. They use sophisticated computer models and real-time observations to try to anticipate these events, but it's still an inexact science.
These eddies also affect marine life, altering nutrient distribution and impacting the food chain. They truly are significant, these swirling pockets of water!

Why Should We Care About All This?
4. Real-World Implications
So, why should you care about the Loop Current "rule" and its eddy-shedding habits? Well, for one thing, it directly affects hurricane forecasting. Accurate predictions of the Loop Current's behavior can help us better anticipate hurricane intensity and track, giving communities more time to prepare and evacuate.
Furthermore, the Loop Current plays a vital role in the Gulf of Mexico's ecosystem. It transports nutrients, influences water temperatures, and affects the distribution of marine life. Understanding the current is essential for managing fisheries, protecting coral reefs, and conserving the Gulf's biodiversity.
The oil and gas industry also has a vested interest in the Loop Current. The current can affect the placement and operation of offshore platforms, and eddies can pose a risk to pipelines and other infrastructure. Knowing where the eddies are headed will have a huge impact for the Oil and Gas industries.
Finally, the Loop Current is connected to the broader global climate system. It plays a role in transporting heat from the tropics towards the poles, influencing weather patterns around the world. It's all interconnected, and understanding the Loop Current helps us understand the bigger picture.

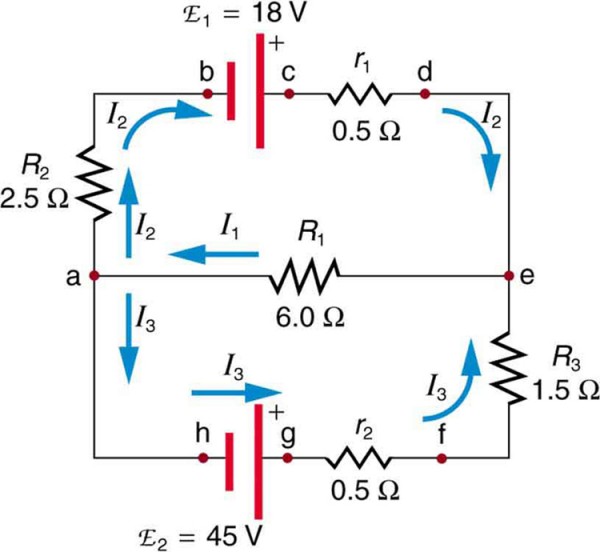
Examples Of Kirchhoff's Law
Beyond the Basics
5. Exploring Further Research
If you're really keen to learn more about the Loop Current, there's a wealth of research out there. Oceanographic institutions like NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) and universities around the Gulf Coast are constantly studying the current, collecting data, and refining their models.
Look for scientific papers published in journals like the Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans or Geophysical Research Letters. These papers delve into the details of the Loop Current's dynamics, eddy formation, and its impact on the Gulf ecosystem.
You can also explore online resources, such as NOAA's website and the websites of various oceanographic research institutions. Many of these sites offer real-time data, animations, and educational materials about the Loop Current.
Understanding the Loop Current truly needs ongoing research and constant study. It is one of the most important things to study if you want to predict the hurricanes and their path!
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered!
Let's tackle some common questions about the Loop Current.
Q: Is the Loop Current getting stronger or weaker due to climate change?
A: The jury's still out on that one! Climate change is a complex beast, and its effects on the Loop Current are still being studied. Some models suggest that the current may weaken due to changes in temperature and salinity, while others suggest that it may strengthen. More research is definitely needed! The impact of this event, if it happen, will be massive!
Q: Can we control the Loop Current?
A: Nope! The Loop Current is a massive force of nature, and there's no practical way to control it (nor should we even try!). We can only study it, understand it, and try to predict its behavior. We can't control the ocean, that's for sure!
Q: How often does the Loop Current shed an eddy?
A: It varies, but typically the Loop Current sheds an eddy every 6 to 11 months. However, the timing can be quite unpredictable, and some years it may shed multiple eddies, while other years it may not shed any at all. That unpredictable pattern is what makes it hard to study the current itself.
Q: What happens to the eddies after they break off from the Loop Current?
A: The eddies slowly drift westward across the Gulf of Mexico, gradually dissipating and mixing with the surrounding waters. They can persist for several months, influencing water temperatures, nutrient distribution, and hurricane intensity along the way. Even though these eddy dissipates over time, the impact they make are not!