Fine Beautiful Tips About Is PLC And CNC The Same

Difference Between PLC And CNC Machine
PLC vs. CNC
1. Decoding the Acronym Jungle
Ever stumbled into the world of manufacturing and felt like you walked into alphabet soup? PLC and CNC are two of the most common acronyms you'll hear buzzing around, but don't let them intimidate you. While they often work side-by-side, they're definitely not twins. Think of them more like colleagues with very different job descriptions. We're here to clear up the confusion and explore what makes each unique.
So, is PLC and CNC the same? The short answer is a resounding no! They serve different purposes within automated systems. This article dives deep into their individual roles, showing you exactly where they shine. We'll even touch on how they collaborate to create efficient and precise manufacturing processes. Consider it your crash course in automation terminology.
Forget dry, technical manuals! We'll break down the complexities in a way that's easy to understand, even if you're not an engineer. Well use everyday analogies, injecting a bit of humor to keep things interesting. By the end, you'll be able to confidently distinguish between PLCs and CNCs, impressing your friends at your next trivia night (or at least holding your own in a technical conversation!).
Prepare to have your automation understanding boosted. No more getting these acronyms mixed up. Let's get started and unravel this mystery together, one step at a time. Think of it as learning to speak another language — the language of machines!
What exactly is a PLC? (Programmable Logic Controller)
2. The Brains Behind the Operation
Imagine a factory assembly line. There are conveyor belts whirring, robotic arms swinging, and sensors detecting the presence of products. Who's orchestrating this complex dance? That's where the PLC comes in. A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is essentially a specialized computer designed to control industrial processes. It's the digital brain that monitors inputs (like sensor readings and button presses) and makes decisions based on programmed logic.
Think of it like this: you set up a series of "if-then" rules for the PLC. "If" the sensor detects a box on the conveyor belt, "then" stop the belt. "If" the temperature reaches a certain level, "then" activate the cooling system. These rules, or "ladder logic," are programmed into the PLC, allowing it to automate repetitive tasks and respond to changing conditions in real-time. It's the automation maestro of the factory floor. It tells the machines what to do.
PLCs are robust and reliable, built to withstand the harsh conditions of industrial environments. They can handle extreme temperatures, vibrations, and electrical noise. Unlike your home computer, which might crash if you spill coffee on it, PLCs are designed for uptime and dependability. This is crucial in manufacturing, where downtime can translate into significant financial losses.
Essentially, PLCs are the workhorses of automation. They are found in a wide variety of industries, from food processing to automotive manufacturing. They are controlling bottling plants, managing traffic lights, and even running amusement park rides. They silently ensure things run smoothly and safely behind the scenes. In a nutshell, PLC's main function is to control the entire process.

CNC Vs PLC What Do They Stand For And Is The Difference? DO
What is a CNC Machine? (Computer Numerical Control)
3. The Precision Artist
Now, let's shift our focus to the CNC machine, or Computer Numerical Control machine. While the PLC is the brain controlling the overall process, the CNC machine is the highly skilled artisan. It's a machine tool, such as a mill or lathe, that is controlled by a computer. This computer uses numerical control to precisely guide the machine's movements, creating complex shapes and parts from raw materials.
Imagine a sculptor carefully chiseling away at a block of marble to create a masterpiece. A CNC machine does something similar, but with incredible precision and speed. Instead of a chisel, it uses cutting tools like drills, mills, or lasers. The computer tells the machine exactly where to move the cutting tool, how fast to move it, and how deep to cut. This level of control allows for the creation of intricate and consistent parts, time after time. You can achieve almost impossible shape to make by hand.
CNC machines are programmed using a language called G-code. This code contains instructions that tell the machine everything it needs to know to create a specific part. Writing G-code can be complex, but modern CNC machines often use Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software to simplify the process. CAM software allows engineers to design parts in a 3D environment and then automatically generate the G-code needed to machine them.
From aerospace components to medical implants, CNC machines are used to manufacture a vast range of products. Their ability to produce highly accurate and repeatable parts makes them essential in industries where precision is critical. They are the masters of precision and efficiency in the manufacturing world, turning digital designs into physical realities. CNC focuses on the cutting, shaping, and drilling.

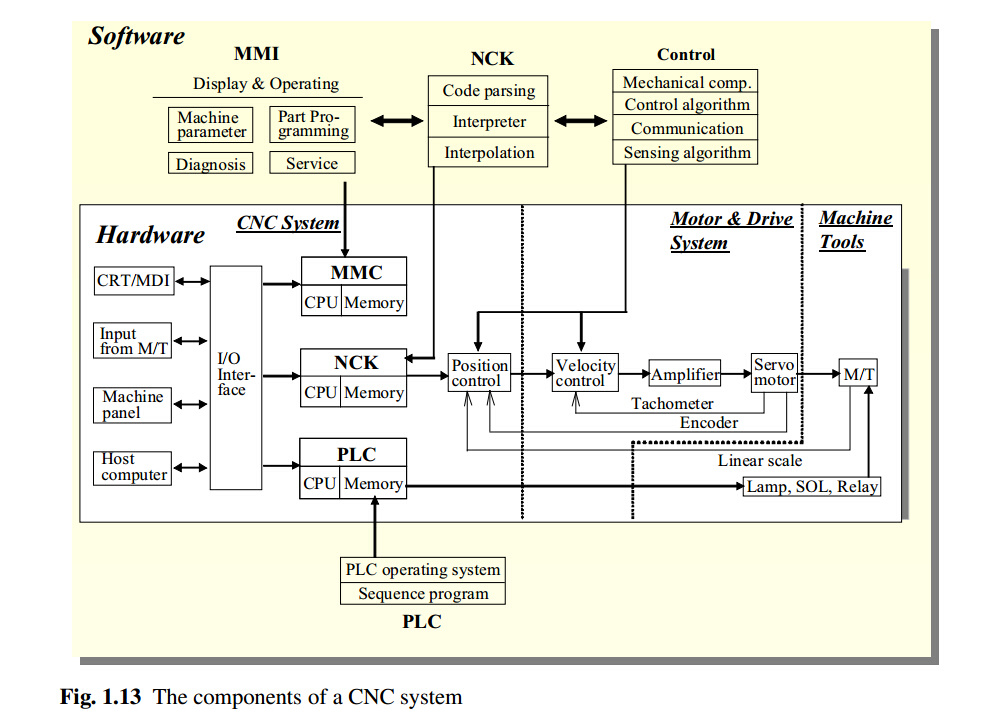
PLC and CNC
4. The Dynamic Duo of Automation
So, PLCs control the overall automated process, and CNC machines carve out complex shapes. But how do they actually work together? This is where the magic happens! They often collaborate to create a seamless and efficient manufacturing workflow. The PLC can be used to control the loading and unloading of materials into the CNC machine, start and stop the machining process, and monitor the machine's performance.
Think of it like a conductor leading an orchestra. The PLC is the conductor, setting the overall tempo and ensuring that all the instruments (the CNC machine and other components) play in harmony. The CNC machine, in turn, is a virtuoso instrument, executing complex melodies (machining operations) with precision and skill. The PLC might tell the CNC machine when to start cutting, what cutting parameters to use, and when to stop. It might also monitor the CNC machine for errors and alert operators if something goes wrong. The operator then fixes the problem and notifies PLC again.
For example, imagine a robotic arm loading metal blanks into a CNC lathe. The PLC controls the robotic arm, ensuring that the blanks are loaded correctly and safely. Once the blank is in place, the PLC signals the CNC lathe to begin machining. During the machining process, the PLC monitors the CNC lathe's performance, checking for things like tool wear and overheating. If any problems are detected, the PLC can stop the machine and alert an operator. This ensures a smooth workflow and saves time.
This collaborative relationship between PLCs and CNC machines results in greater efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility in manufacturing processes. By automating these tasks, manufacturers can reduce labor costs, improve product quality, and respond more quickly to changing market demands. They are a powerful duo driving innovation and efficiency in the modern manufacturing landscape.

Key Differences in a Nutshell
5. Quick Recap for Clarity
Okay, let's hammer home the key differences between PLCs and CNC machines. The PLC is the brain; it controls the overall automated process. It monitors sensors, makes decisions based on programmed logic, and tells other machines what to do. It's a general-purpose controller used for a wide range of applications.
On the other hand, the CNC machine is the precision artist; it's a machine tool controlled by a computer. It uses numerical control to precisely guide the machine's movements, creating complex shapes and parts from raw materials. Its a specialized tool designed for precise machining operations. You can picture PLC as software and CNC as hardware.
Think of it this way: the PLC is the traffic controller, directing the flow of vehicles (materials and processes) through the factory. The CNC machine is the skilled driver, precisely navigating a specific route (machining operation) to reach a destination (finished part). One manages the grand scheme; the other executes a specialized task within that scheme.
Finally, to re-iterate, CNC and PLC has important differences. They are crucial parts of the automated system. PLC is the central command of the entire process. CNC machine is the one that process the material based on command by PLC.

FAQ
6. Clearing Up Lingering Doubts
Even with all that explanation, some questions might still linger. Let's tackle a few common inquiries to ensure complete clarity.
Q: Can a PLC replace a CNC machine?A: Nope. They have different roles. A PLC can control a CNC machine, but it can't be a CNC machine. A PLC handles the overall automation, while a CNC executes precise machining.
Q: Can a CNC machine operate without a PLC?A: Technically, yes, especially for simple tasks. But for complex, integrated systems, a PLC is usually essential for coordinating the CNC machine with other parts of the process.
Q: Which is harder to learn, PLC programming or CNC programming (G-code)?A: It depends on your background and aptitude. Both require specialized knowledge. Some find ladder logic (PLC programming) more intuitive, while others prefer the precision and structure of G-code. It's often down to personal preference!
Q: What are the future trends for PLC and CNC?A: The future of both PLC and CNC technology involves increasing integration with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), cloud-based systems, and advanced data analytics. We're also seeing advancements in AI-powered programming and predictive maintenance. Expect more intelligent, connected, and efficient manufacturing processes!