Best Info About How Fast Is 1 Petabit
Let's Talk Petabits
1. Understanding the Petabit in Simple Terms
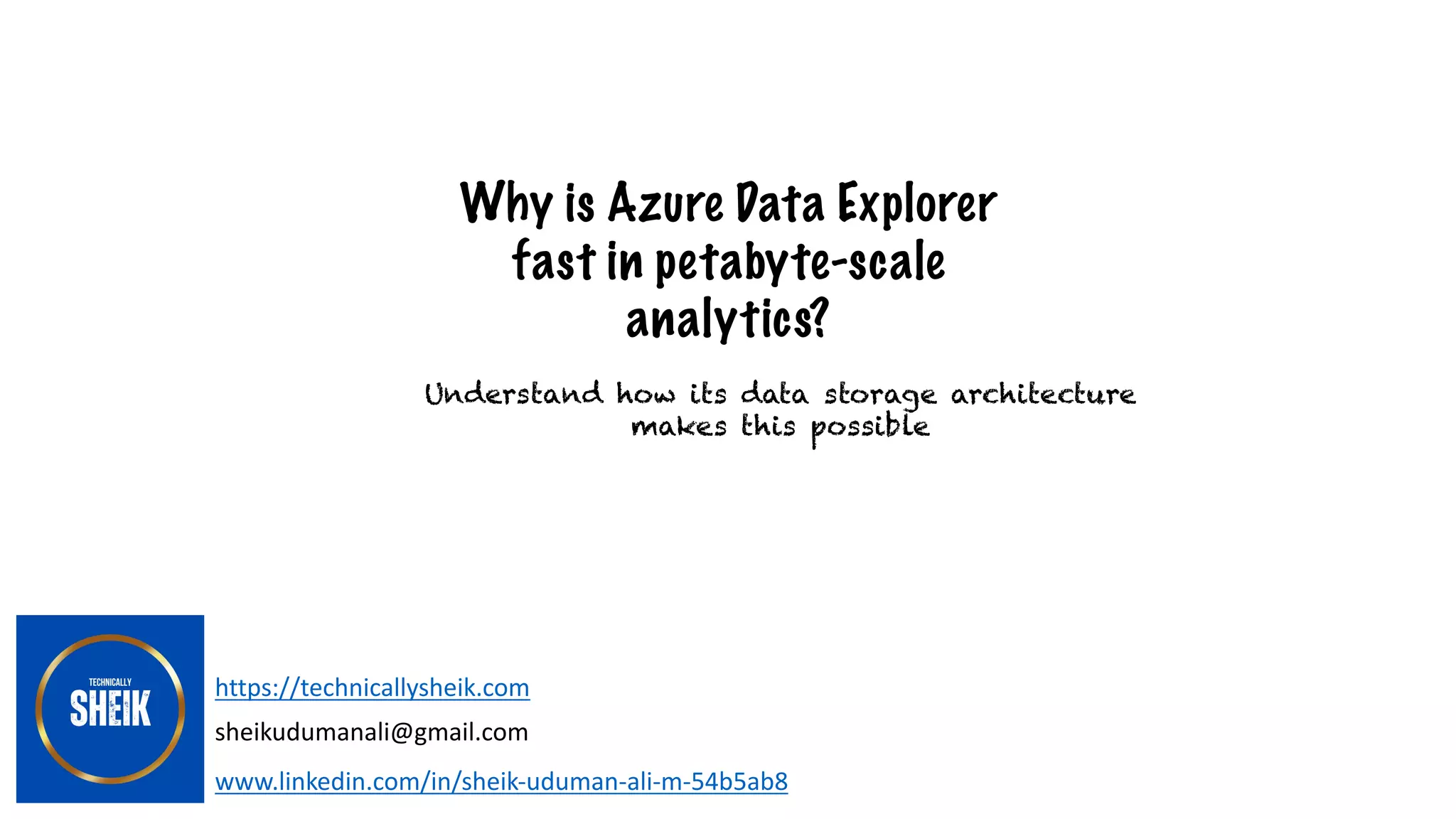
Okay, so you've heard the term "petabit" thrown around, probably in some techy conversation about internet speeds or data storage. But what does it really mean? Well, let's break it down. Think of it like this: a bit is the smallest unit of data, like a single letter in a giant book. Now, a petabit is like having a library full of those giant books. We're talking a lot of data. To be precise, 1 petabit is equal to 1,000,000,000,000,000 bits, or 10^15 bits. That's a one followed by fifteen zeros. Try counting that out loud; I dare you!
So, it's big. Really big. But understanding the number itself isn't quite enough. To really grasp the speed, we need to put it into context, which is where the fun begins. Imagine trying to download every movie ever made. A petabit gives you a fighting chance (depending on your internet connection, of course, and how quickly they're making new movies these days).
The key takeaway is that a petabit signifies a colossal amount of data and, when we're talking about transfer speeds, an equally impressive rate of data transmission. We're not dealing with your grandpa's dial-up modem here; we're in warp-speed territory.
Consider this: even transferring a fraction of a petabit can impact networks, infrastructure and require robust system. That's why it is often used to define large-scale data operations or the capabilities of sophisticated technologies. The power of a petabit is genuinely something to behold.

Putting the Petabit into Perspective
2. Comparing Petabits to Everyday Internet
Alright, so we know a petabit is enormous. But let's ground this in reality. Your home internet probably isn't measured in petabits per second (Pbps). More likely, you're dealing with megabits per second (Mbps) or gigabits per second (Gbps). A gigabit is one billion bits, which is significantly smaller than a petabit (one quadrillion bits).
To put it in perspective, 1 petabit is equal to 1,000 terabits (Tb), which is equal to 1,000,000 gigabits (Gb). Even the fastest commercially available internet connections barely scratch the surface of petabit speeds. We're talking about a whole different order of magnitude here.
So, where do we see petabit speeds in action? Primarily in the backbone of the internet, in massive data centers, and in cutting-edge research facilities. These are the places that require handling vast amounts of data quickly and efficiently. Think about streaming services, large cloud providers, or scientific simulations that generate terabytes or even petabytes of data.
Imagine a global network that can transfer entire libraries in the blink of an eye. This kind of speed underpins many applications that affect our lives on a daily basis. From cloud storage to streaming, petabit speed is there to facilitate it. It is also important to bear in mind that achieving true petabit speeds requires significant infrastructure investment.

SSD 1 Petabyte Sắp Thành Hiện Thực
The Future is Fast
3. Petabit Technology and Innovation
Now, let's peek into the crystal ball and see where petabit speeds are headed. As data demands continue to explode, the need for even faster networks becomes increasingly critical. We're talking about technologies like 5G and beyond, the ever-expanding Internet of Things (IoT), and the rise of artificial intelligence (AI) — all of these are driving the demand for petabit-scale connectivity.
Innovations in fiber optics, network infrastructure, and data compression techniques are constantly pushing the boundaries of what's possible. Researchers and engineers are working tirelessly to develop new ways to transmit and process data faster and more efficiently. This involves using new materials, advanced modulation techniques, and sophisticated algorithms.
Think about the potential impact of petabit speeds on fields like medical imaging, scientific research, and autonomous vehicles. Imagine being able to transmit massive medical datasets in seconds, enabling faster diagnoses and treatment plans. Or consider the ability to run complex simulations in real-time, accelerating scientific discoveries and technological breakthroughs.
The quest for petabit speeds isn't just about bragging rights; it's about unlocking new possibilities and transforming the way we live and work. While the average user might not directly interact with petabit speeds, the underlying benefits trickle down in terms of better service, faster reaction and greater capacity.

Is It Dead Optical Drives?!
Practical Applications
4. How Petabit Speeds Shape the Modern World
Beyond the technical jargon, how do petabit speeds actually shape our daily lives? The impact is more profound than you might think. Consider the vast data centers that power the internet, which are humming away, processing and storing colossal amounts of information. Petabit networks are essential for these data centers to function efficiently, ensuring that your emails, videos, and social media posts are delivered quickly and reliably.
Cloud computing relies heavily on high-speed data transfer, and petabit networks are the backbone of these services. Whether you're storing files on the cloud, running applications remotely, or collaborating with colleagues on a project, you're benefiting from the speed and capacity of petabit technology. Furthermore, the rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are driving the need for faster data processing.
Self-driving cars, for example, generate enormous amounts of data from sensors and cameras, which need to be processed in real-time. Petabit networks can provide the necessary bandwidth and low latency to support these applications, making them safer and more efficient. In short, petabit speeds are becoming increasingly vital to our digital society.
From enabling global communication to supporting emerging technologies, petabit networks are a key enabler of progress. While you might not see the direct benefit of it, it is what keeps the world in the digital form as we know it today.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
5. Common Questions About Petabits Answered
Let's address some common questions people have about petabits:
Q: Will I ever have petabit internet at home?
A: Not likely in the immediate future. The cost and infrastructure requirements are currently too high for residential applications. However, as technology evolves and costs decrease, it's certainly possible that petabit speeds could become more accessible in the long term.
Q: What's the difference between a petabit and a petabyte?
A: A petabit (Pb) is a unit of data transfer rate (speed), while a petabyte (PB) is a unit of data storage (capacity). Think of it like this: petabits are how fast the water flows through a pipe, while petabytes are how much water the pipe can hold.
Q: What are the biggest challenges in achieving widespread petabit speeds?
A: Several challenges exist, including the cost of upgrading infrastructure, the need for more efficient data compression techniques, and the development of new technologies for transmitting and processing data at such high speeds. Overcoming these challenges requires ongoing research, innovation, and investment.
Q: Is 1 petabit per second fast enough?
A: Currently 1 petabit is exceptionally fast. But technology never sleeps and with the ever increasing data demands, research continues to increase data speed and efficiency.