Wonderful Info About CAN Bus Vs Fd
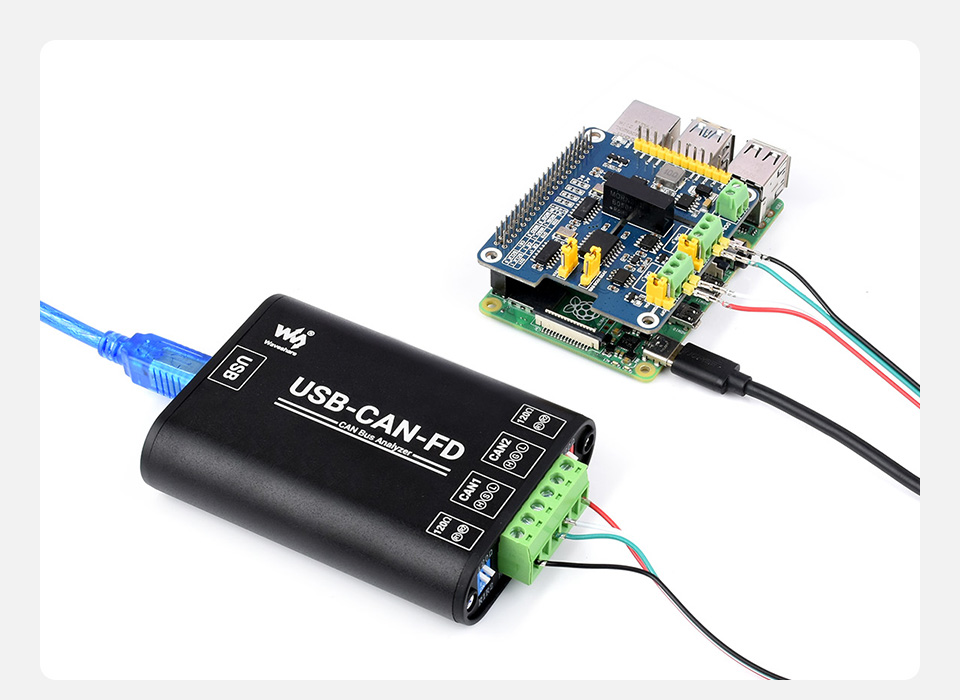

Industrial Grade CAN/CAN FD Bus Data Analyzer
Decoding CAN Bus vs. CAN Bus FD
1. Speed Demons and Data Wranglers
Ever wondered how all those complex systems in your car talk to each other? The answer, more often than not, involves something called a CAN bus. Think of it as the central nervous system of your vehicle, allowing different electronic control units (ECUs) to communicate seamlessly. But like any good technology, it's evolved over time. Enter CAN FD, or CAN with Flexible Data-Rate. So, what's the big deal? Let's dive into the world of automotive networking and see what makes CAN FD tick differently from its older sibling, the classic CAN bus.
At its core, the CAN bus is a robust and reliable communication protocol. It's been a workhorse in the automotive industry for decades, handling everything from engine management to anti-lock braking systems. The beauty of the CAN bus lies in its simplicity and resilience. It operates at a relatively low speed, typically up to 1 Mbps, and uses a clever arbitration scheme to prevent data collisions. This makes it ideal for safety-critical applications where reliable communication is paramount. However, as cars become more complex and data-hungry, the limitations of the classic CAN bus become apparent.
Modern vehicles are packed with sensors, cameras, and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). All this data needs to be transmitted and processed quickly, and the traditional CAN bus simply can't keep up. This is where CAN FD steps in. It's designed to handle the increased bandwidth requirements of modern automotive applications. But how does it achieve this? Well, that's where the "flexible data-rate" part comes into play. CAN FD allows for higher data rates and larger data payloads, making it a much more efficient communication protocol for today's complex vehicles.
Think of it this way: classic CAN bus is like a one-lane country road, perfect for a leisurely drive. CAN FD, on the other hand, is like a multi-lane highway, allowing for much faster and more efficient traffic flow. While both serve the purpose of getting you from point A to point B, CAN FD is clearly better suited for handling the demands of modern high-speed data communication. It's not just about speed, though; it's also about the amount of data that can be transmitted in each message. We'll explore that further in the next section.

Key Differences
2. Digging into the Details
Alright, let's get down to the nitty-gritty (oops, almost slipped up there!). The primary differences between CAN bus and CAN FD boil down to two main areas: speed and data payload. As mentioned earlier, CAN FD supports significantly higher data rates than the classic CAN bus. While the standard CAN bus typically operates at speeds up to 1 Mbps, CAN FD can reach speeds of up to 8 Mbps, and even higher in some implementations. That's a substantial increase, allowing for much faster data transmission.
But it's not just about raw speed. CAN FD also allows for larger data payloads. The classic CAN bus is limited to a maximum data payload of 8 bytes per message. CAN FD, on the other hand, can support payloads of up to 64 bytes. This means that more data can be transmitted in a single message, reducing the overhead associated with message transmission and improving overall communication efficiency. Imagine trying to move a house one brick at a time versus moving entire walls at once; CAN FD is definitely moving the walls!
Another key difference lies in the error detection mechanisms. CAN FD incorporates improved error detection and correction capabilities, making it even more robust and reliable than the classic CAN bus. This is particularly important in safety-critical applications, where data integrity is paramount. While both CAN bus and CAN FD use Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) for error detection, CAN FD employs a more sophisticated CRC algorithm, providing enhanced protection against data corruption.
The increased speed, larger data payloads, and improved error detection capabilities of CAN FD make it a superior communication protocol for modern automotive applications. However, it's important to note that CAN FD is not a drop-in replacement for the classic CAN bus. It requires new hardware and software, and existing CAN bus networks need to be upgraded to support it. But the benefits of CAN FD are well worth the effort, particularly in applications that require high-speed data communication and large data payloads.

Advantages and Disadvantages
3. The Good, the Bad, and the Bandwidth
Like any technology, CAN bus and CAN FD each have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. The classic CAN bus has a long history of reliability and is well-established in the automotive industry. It's relatively simple to implement and is supported by a wide range of hardware and software tools. Its robustness and proven track record make it a suitable choice for many applications, particularly those where cost is a major concern.
However, the limitations of the classic CAN bus become apparent in applications that require high-speed data communication. Its relatively low data rate and small data payload can be a bottleneck in modern vehicles with numerous sensors and advanced driver-assistance systems. Furthermore, the increasing complexity of automotive systems demands more efficient communication protocols that can handle larger amounts of data with minimal overhead. This is where CAN FD shines, offering significantly higher data rates and larger data payloads, making it a more efficient communication protocol for today's complex vehicles.
The main disadvantage of CAN FD is its increased complexity and cost. It requires new hardware and software, and existing CAN bus networks need to be upgraded to support it. This can be a significant investment, particularly for manufacturers who have already invested heavily in classic CAN bus technology. Furthermore, CAN FD is not as widely supported as the classic CAN bus, and the availability of tools and expertise may be limited in some areas. It's like choosing between a reliable old tractor and a brand-new, high-tech combine harvester: the tractor is cheaper and simpler, but the combine can handle a much bigger job.
Ultimately, the choice between CAN bus and CAN FD depends on the specific requirements of the application. If you need a robust and reliable communication protocol for safety-critical applications and cost is a major concern, the classic CAN bus may be a suitable choice. However, if you need high-speed data communication and large data payloads to support advanced automotive systems, CAN FD is the way to go. Weighing the advantages and disadvantages of each technology will help you make an informed decision and choose the best communication protocol for your needs. It's all about finding the right tool for the job!

Real-World Applications
4. From Engine Control to Autonomous Driving
So, where exactly do we see these technologies in action? The classic CAN bus is widely used in a variety of automotive applications, including engine management systems, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), airbags, and body control modules (BCMs). It's also used in industrial automation, medical equipment, and other applications where reliable communication is essential. Because of its proven reliability, cost-effectiveness and widespread support, it remains a staple for many established automotive and industrial solutions.
CAN FD, on the other hand, is primarily used in applications that require higher bandwidth and larger data payloads. This includes advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment systems, and autonomous driving systems. It's also finding its way into electric vehicles (EVs), where the increased data rates and larger payloads are needed to manage complex battery management systems and motor control systems. The ability to handle larger volumes of data at greater speeds makes CAN FD a key enabler for cutting-edge features in modern vehicles.
Consider an ADAS system, for example. It relies on a multitude of sensors, including cameras, radar, and lidar, to perceive the environment around the vehicle. All this sensor data needs to be processed and transmitted quickly to enable features such as automatic emergency braking, lane keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control. The higher bandwidth and larger payloads of CAN FD are essential for handling this data efficiently and ensuring the safe and reliable operation of these systems. Essentially, CAN FD empowers these systems to react swiftly and effectively.
In summary, while the classic CAN bus remains a reliable choice for many established applications, CAN FD is rapidly becoming the preferred communication protocol for modern automotive systems that require high-speed data communication and large data payloads. As vehicles become increasingly complex and autonomous, the importance of CAN FD will only continue to grow. It's the backbone of the intelligent, connected cars of the future, enabling the safe and efficient operation of all the amazing features we're starting to see on the road today.

Future Trends
5. Beyond CAN
The world of automotive networking is constantly evolving, and new technologies are emerging to meet the ever-increasing demands of modern vehicles. While CAN bus and CAN FD remain important communication protocols, they are not the only players in the game. Ethernet, for example, is gaining popularity in automotive applications, particularly for high-bandwidth applications such as camera systems and infotainment systems. Its ability to handle massive amounts of data makes it a natural fit for these demanding use cases.
Another emerging technology is Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN), which provides deterministic communication over Ethernet. This is particularly important for safety-critical applications, where timing is paramount. TSN ensures that data is delivered within a guaranteed timeframe, making it suitable for applications such as autonomous driving and advanced driver-assistance systems. It adds a layer of predictability that's essential for safe and reliable operation. Think of it as adding traffic lights and strict speed limits to an already fast highway.
The future of automotive networking is likely to involve a combination of different communication protocols, each optimized for specific applications. CAN bus and CAN FD will continue to play a role in safety-critical applications and body control functions, while Ethernet and TSN will be used for high-bandwidth applications and time-critical tasks. The challenge will be to integrate these different technologies seamlessly and efficiently, ensuring that all the various systems in the vehicle can communicate effectively. It's all about creating a harmonious symphony of communication, where each instrument plays its part perfectly.
Furthermore, cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important in automotive networking. As vehicles become more connected, they become more vulnerable to cyberattacks. Protecting the vehicle's communication network from unauthorized access and malicious attacks is essential for ensuring the safety and security of the vehicle and its occupants. Future automotive networking technologies will need to incorporate robust security measures to mitigate these risks and ensure the integrity of the vehicle's data. It's like building a fortress around the car's nervous system, protecting it from external threats.
Industrial Grade CAN/CAN FD Bus Data Analyzer, USB To CAN Adapter
Frequently Asked Questions
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Still have some questions swirling around? Let's tackle a few of the common ones:
Q: Is CAN FD just a faster version of CAN bus?A: Not just faster. While speed is a major difference, CAN FD also offers larger data payloads and improved error detection. It's more like a complete overhaul than a simple upgrade.
Q: Can I replace my existing CAN bus system with CAN FD?A: It's not a direct swap. CAN FD requires different hardware and software, so it's more of a planned upgrade rather than a simple replacement. Think of it like renovating a kitchen ' you can't just replace the sink and call it a day!
Q: Will CAN bus become obsolete?A: Not likely anytime soon. The classic CAN bus is still widely used in many applications, particularly where cost and simplicity are important factors. While CAN FD is gaining ground, CAN bus isn't going anywhere fast. It's a reliable workhorse that will continue to serve its purpose for years to come.
Q: Is CAN FD more secure than CAN bus?A: While CAN FD includes improved error detection, neither CAN bus nor CAN FD inherently provides robust security features against cyberattacks. Security needs to be implemented at a higher level, regardless of the underlying communication protocol.